B-hCFB mice plus
| Strain Name |
C57BL/6JNifdc-Cfbtm3(CFB)Bcgen/Bcgen |
Common Name | B-hCCL17 mice |
| Background | C57BL/6JNifdc | Catalog number | 113153 |
|
Aliases |
BF, FB, BFD, GBG, CFAB, CFBD, PBF2, AHUS4, FBI12, H2-Bf, ARMD14 | ||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
629 | ||
- The CFB gene encodes complement factor B, which is a component of the alternative pathway of complement activation. Factor B is mainly synthesized in the liver and secreted into the plasma. In the presence of Mg++, Factor B binds to C3b to form the C3bB complex. This complex can be activated by cleavage of the Factor B portion by Factor D, resulting in the release of the Ba fragment of Factor B while the Bb fragment remains bound to C3b. The C3bBb complex functions as a C3 and C5 convertase due to the serine protease activity of the Bb fragment. The presence of the split products, the Ba and Bb fragments of Factor B, indicates that the alternative complement pathway has been activated.
- The exons 1~18 of the mouse Cfb gene that encoded the full-length protein were replaced by human CFB exons 1~18 in B-hCFB mice. The promoter, 5’UTR and 3’UTR region of the mouse gene are replaced by human counterparts. The human CFB expression is driven by human CFB promoter, while mouse Cfb gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
- Mouse Cfb mRNA was detected in C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and heterozygous B-hCFB mice (H/+). Human CFB mRNA was exclusively detected in heterozygous B-hCFB mice (H/+), but not in wild-type mice. The human CFB was exclusively detected in homozygous B-hCFB mice (H/H).
Gene targeting strategy for B-hCFB mice plus. The exons 1~18 of the mouse Cfb gene that encoded the full-length protein were replaced by human CFB exons 1~18 in B-hCFB mice. The promoter, 5’UTR and 3’UTR region of the mouse gene are replaced by human counterparts. The human CFB expression is driven by human CFB promoter, while mouse Cfb gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
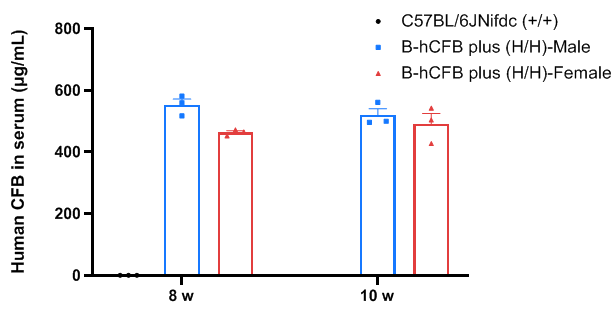
Strain CFB expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice and homozygous B-hCFB mice plus by ELISA. Serum was collected from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCFB mice plus (H/H). The protein expression level of CFB was analyzed by ELISA (Abcam, ab137973). Human CFB was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCFB mice plus (H/H).
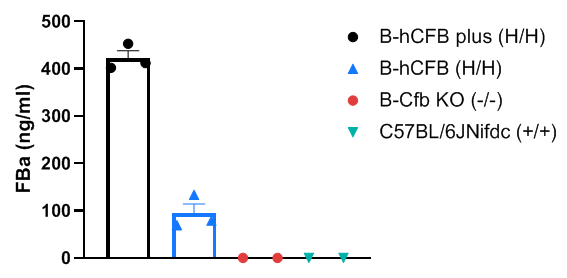
Strain-specific FBa expression analysis in homozygous B-hCFB mice plus by ELISA. Serum were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+), B-Cfb KO mice (-/-), homozygous B-hCFB mice (H/H), and B-hCFB mice plus (H/H) (Male, 7 weeks old) and analyzed by ELISA with FBa ELISA kit (Quidel, A033). FBa was detectable in homozygous B-hCFB mice and B-hCFB mice plus, but not in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice.
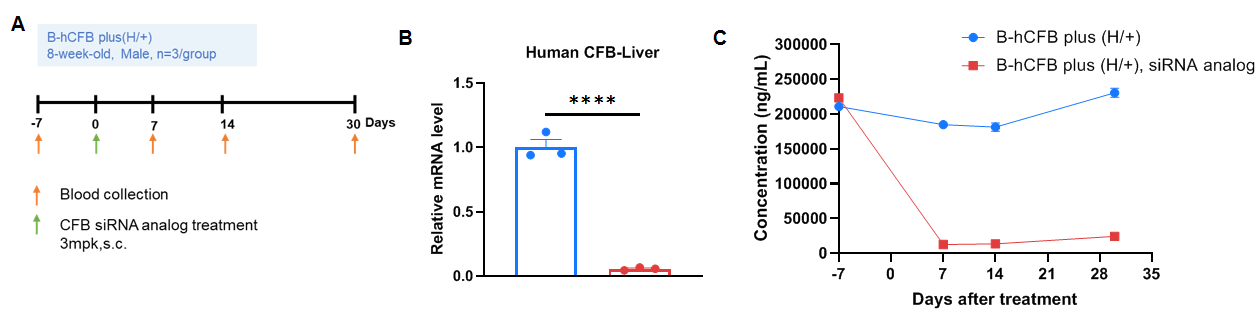
The inhibitory efficiency of the nucleic acid drugs against human CFB in B-hCFB mice plus. B-hCFB mice plus (H/+) were randomly divided into two groups (n=3/group, 8 weeks old, male). The human CFB-targeted siRNA-analog synthesized according to patents and PBS were administered to the mice individually. (A) The schematic diagram of experimental processing. (B) The mice were sacrificed on day 7, the liver tissues were collected to detect the expression level of human CFB mRNA by qPCR. (C) The expression of human CFB protein in serum. The human CFB in the treatment group was significantly reduced compared to the control group. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by t-test. ****p < 0.0001.










 京公网安备:
京公网安备: