| Strain Name | C57BL/6-Il4tm2(IL4)BcgenIl4ratm1(IL4RA)Bcgen/Bcgen | Common Name | B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice |
| Background | C57BL/6 | Catalog number | 120551 |
|
Related Gene |
BCGF-1, BCGF1, BSF-1, BSF1, IL-4 CD124, IL-4RAA, IL4R |
||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
16189,16190 | ||
mRNA expression analysis
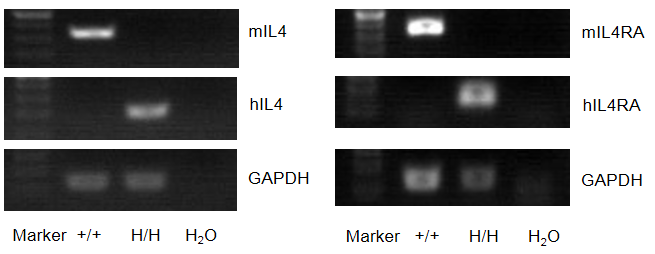
Strain specific analysis of IL4 and IL4RA gene expression in WT and B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice by RT-PCR. Mouse Il4 and Il4ra mRNA was detectable in splenocytes of wild-type (+/+) but not in homozygous B-hIL4/hIL4R mice (H/H) mice. Human IL4 and IL4RA mRNA was detectable only in homozygous B-hIL4/hIL4R mice but not in wild-type mice.
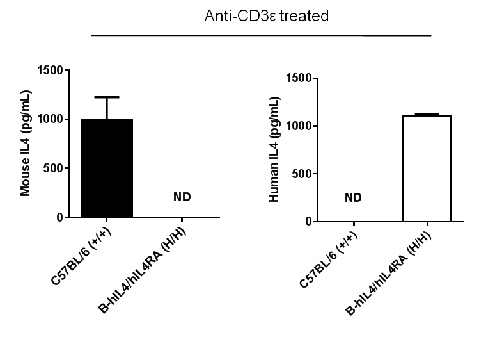
Strain specific IL4 expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice by ELISA. Serum were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice (H/H) stimulated with anti-mouse CD3ε antibody (37.5 μg/mL, 200 μL/mouse, i.p.) for 1.5 hrs in vivo (female, 6-8 weeks old, n=3). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse IL4 antibody (Biolegend, 431104) and anti-human IL4 antibody (Biolegend, 430307) by ELISA. Mouse IL4 was only detectable in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Human IL4 was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice, but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.

Strain specific IL4RA expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice (H/H) stimulated with anti-mouse CD3ε antibody (37.5 μg/mL, 200 μL/mouse, i.p.) for 1.5 hrs in vivo (female, 8-week-old, n=2). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse IL4RA antibody (Biolegend, 144804) and anti-human IL4RA antibody (Biolegend, 355003) by flow cytometry. Mouse IL4RA was only detectable in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Human IL4RA was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice, but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
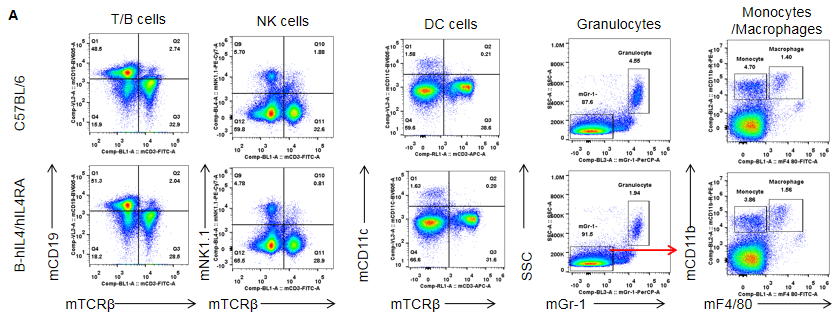
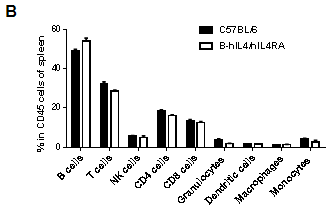
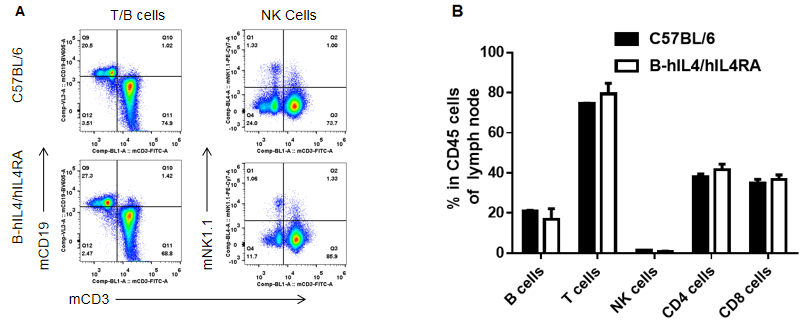
Analysis of spleen leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Splenocytes were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice (n=3, 10-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for CD45 population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T, B, NK, Monocyte, DC and macrophage cells in homozygous B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that introduction of hIL4 and hIL4RA in place of its mouse counterpart does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in spleen.
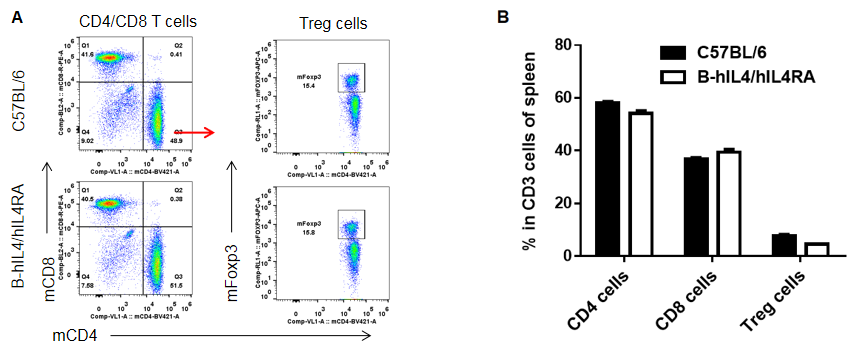
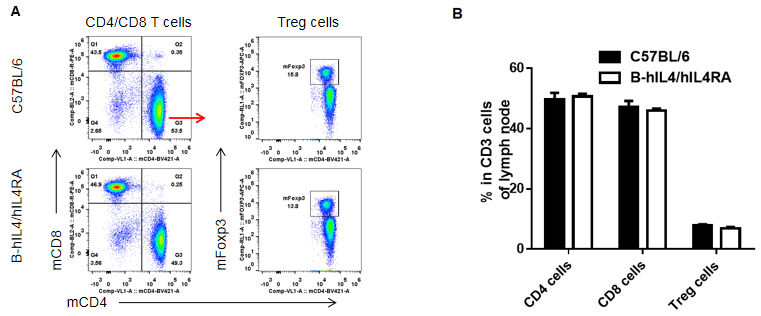
Analysis of subpopulation of T cells in lymph node by FACS. Lymph node were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice (n=3, 10-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the lymph node was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live CD45+ T cells were used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of CD8, CD4, and Treg cells in homozygous B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that introduction of hIL4 and hIL4RA in place of its mouse counterpart does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes in lymph node. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
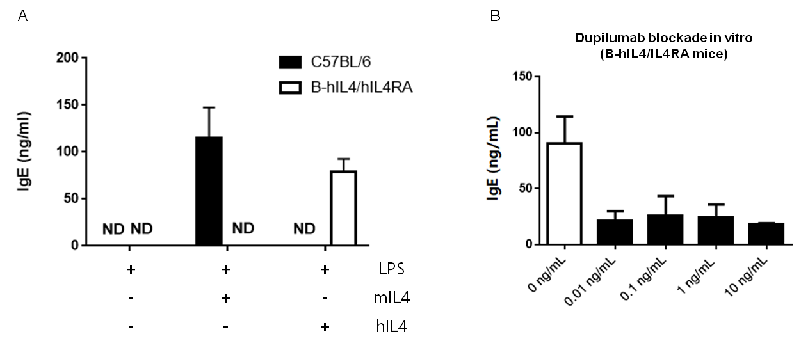
(A) Splenic B cells from C57BL/6 and B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice were cultured with LPS alone or together with 50ng/mL mIL-4/hIL-4. Culture supplements were harvested on day 6 for quantification of IgE by ELISA.(B) Splenic B cells from B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice were incubated with increasing doses of dupilumab (in house) for half of an hour before adding LPS and hIL-4 (50 ng/mL). Culture supernatant was harvested on day 6 for quantification of IgE by ELISA. The result show that B cells from B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice responded well to LPS and IL-4 with IgE production, as similar to C57BL/6 mice. Dupilumab (in house) could effectively block the expression of IgE.
Dupilumab significantly inhibited the activation of B cells induced by hIL4 in B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice
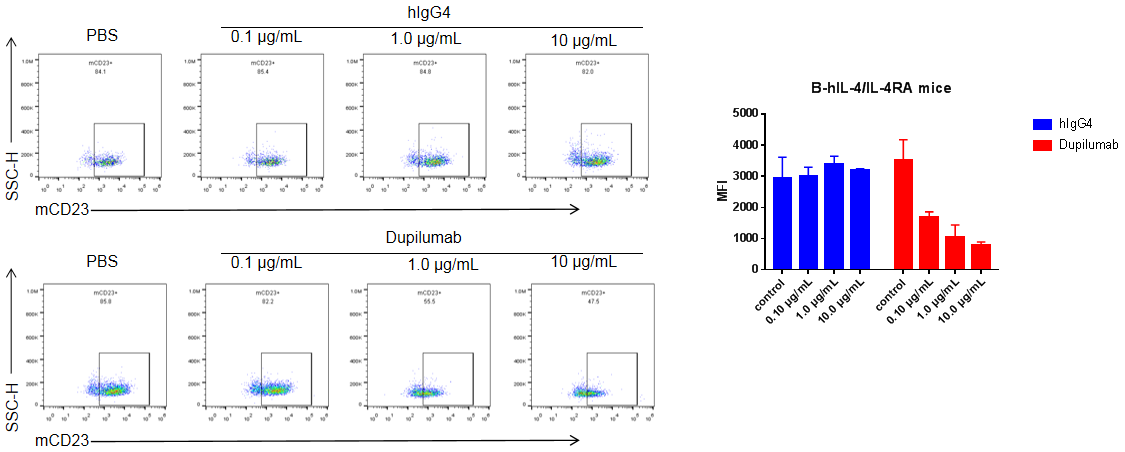
Analysis of activity of B cells in spleen by FACS. Splenocytes were isolated from B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice and incubated with varying concentrations of IgG4 or dupilumab for half an hour. Adding human IL4 (50 pM) for 72 hours and analyzing the activity of B cells. The dupilumab group showed an effect to block B cell activation in B-hIL4/IL4RA mice and showed a dose-dependent effect; the control hIgG4 did not show an effect on block B cell activation.
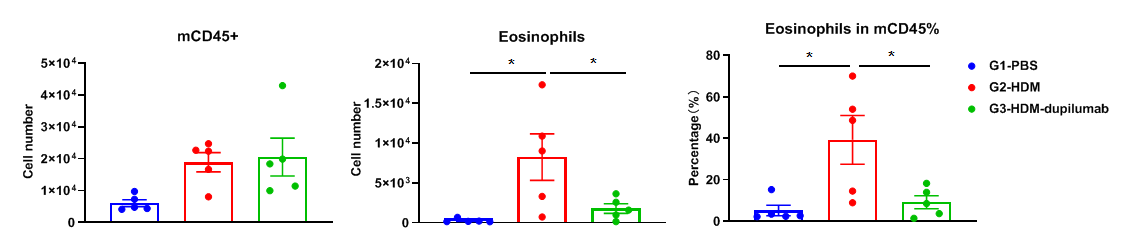
The number of BALF immune cells in mouse asthma model
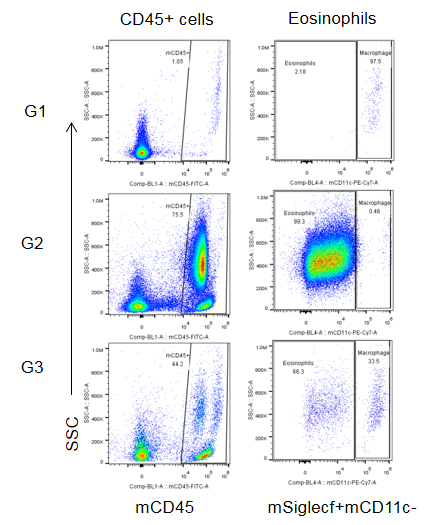
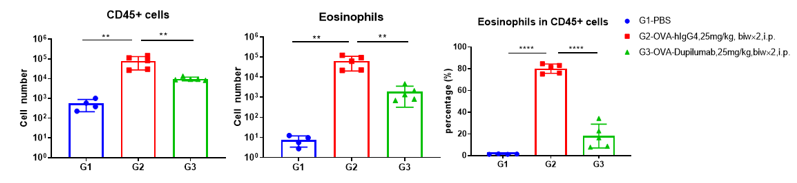
Analysis of immune cells in BALF by FACS. BALF immune cells were isolated from B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice (n=4 or n=5). The number and proportion of eosinophils were analyzed by flow cytometry under the treatment of PBS/dupilumab (in house). After treatment of dupilumab (in house), the number of CD45+ cells and eosinophils were much lower than the positive control in homozygous B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice.
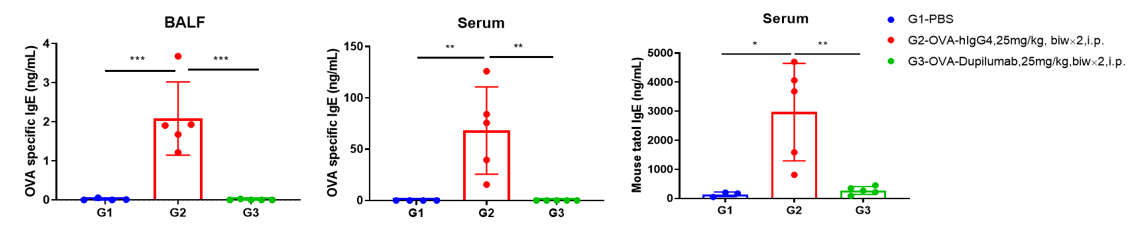
OVA specific and total IgE production in serum and BALF of mouse asthma model
H&E staining in asthma-like model in B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice
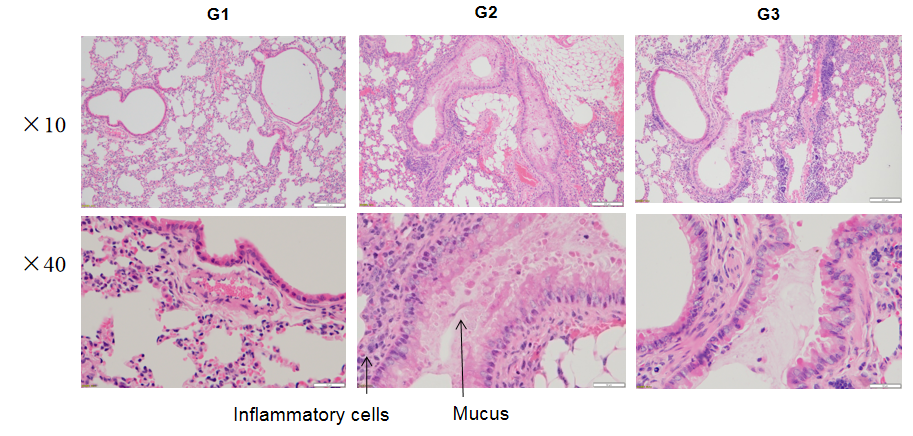
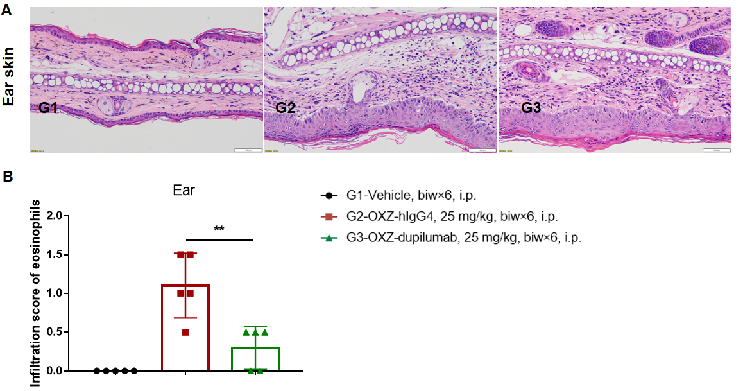
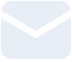
H&E staining of asthma-like model in B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice. Lung tissues were collected at the study endpoint. H&E staining results showed that the lung tissues from B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice exposed to PBS aerosols did not show any inflammation. OVA exposure resulted in a significant increase in peribronchial and perivascular inflammation in B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice. A significant reduction in eosinophils infiltration was observed in mice treated with dupilumab (in house).
Asthma model introduction
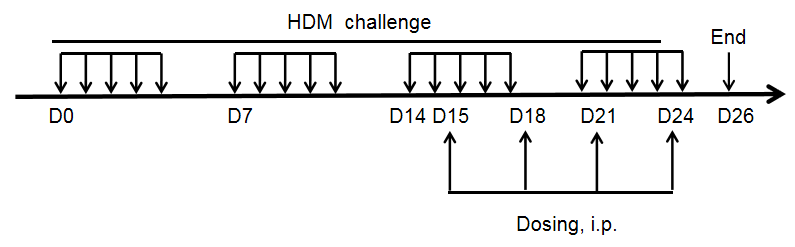
Establishment of asthma mouse model- HDM-induced acute asthma model
Modeling reagent:50 μg HDM in 50 μl PBS (intranasally, i.n.)
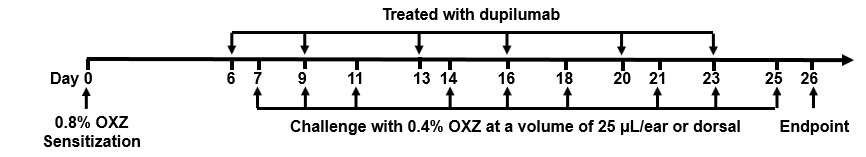
Modeling paradigm:
Efficacy assessment of anti-human IL4RA antibody in mouse asthma model induced with HDM
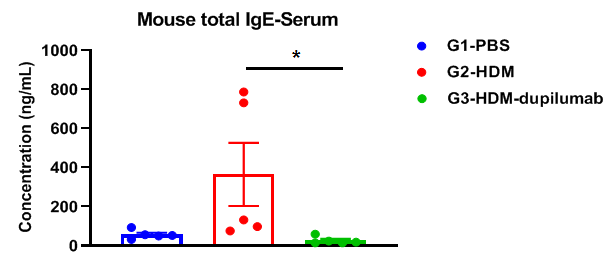
Detection of IgE levels in serum of asthmatic mouse model. Serum was taken at the end of the experiment and total IgE levels were measured using ELISA in serum. The results showed that the levels of total IgE in G2 model group were significantly increased compared with G1 control group, suggesting successful modeling. Total IgE levels were significantly lower after administration of dupilumab (in house) drug compared with the G2 modeling group.
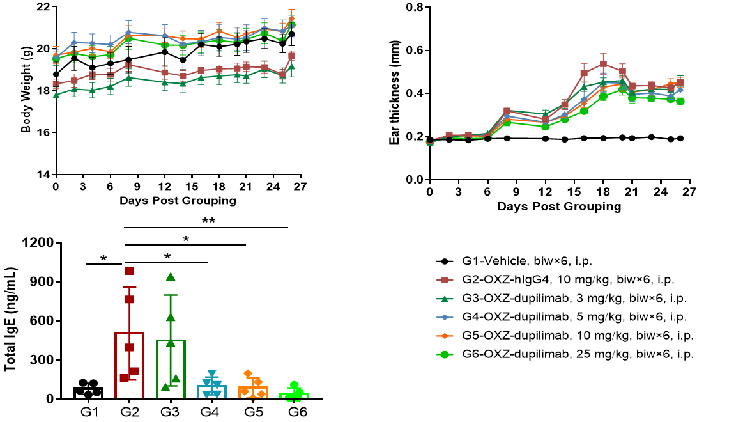


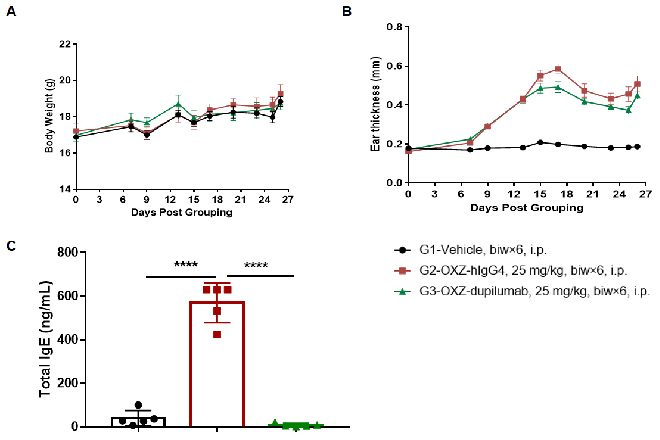










 京公网安备:
京公网安备: