B-hCD16A mice plus
| Strain Name |
C57BL/6N-Fcgr4tm3(FCGR3A)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name | B-hCD16A mice plus |
| Background | C57BL/6N | Catalog Number | 112446 |
|
Aliases |
CD16, FCG3, CD16A, FCGR3, IGFR3, IMD20, FCR-10, FCRIII, CD16-II, FCGRIII, FCRIIIA, FcGRIIIA |
||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
2214 | ||
- This gene encodes a receptor for the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G, and it is involved in the removal of antigen-antibody complexes from the circulation, as well as other responses, including antibody dependent cellular mediated cytotoxicity and antibody dependent enhancement of virus infections. This gene (FCGR3A) is highly similar to another nearby gene (FCGR3B) located on chromosome 1. The receptor encoded by this gene is expressed on natural killer (NK) cells as an integral membrane glycoprotein anchored through a transmembrane peptide, whereas FCGR3B is expressed on polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) where the receptor is anchored through a phosphatidylinositol (PI) linkage. Mutations in this gene are associated with immunodeficiency 20, and have been linked to susceptibility to recurrent viral infections, susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus, and alloimmune neonatal neutropenia. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene..
- The exons 1-5 of mouse Fcgr4 gene that encode signal peptide, extracellular domain and transmembrane domain are replaced by human counterparts in B-hCD16A mice plus. The genomic region of mouse Fcgr4 gene that encodes cytoplasmic portion is retained. The promoter and 5’UTR region of the mouse gene are replaced by human counterparts.
- Human CD16A was detected in NK cells, granulocytes, monocytes and macrophages. We predicate that CD16A has similar expression pattern between human and B-hCD16A mice plus.
- B-hCD16A mice plus provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of CD16A-targeted antibodies.
- Application: this product is used for pharmacodynamics and safety evaluation of CD16A-targeted antibodies for cancers.
Gene targeting strategy for B-hCD16A mice plus. The exons 1-5 of mouse Fcgr4 gene that encode signal peptide, extracellular domain and transmembrane domain are replaced by human counterparts in B-hCD16A mice plus. The genomic region of mouse Fcgr4 gene that encodes cytoplasmic portion is retained. The promoter and 5’UTR region of the mouse gene are replaced by human counterparts.
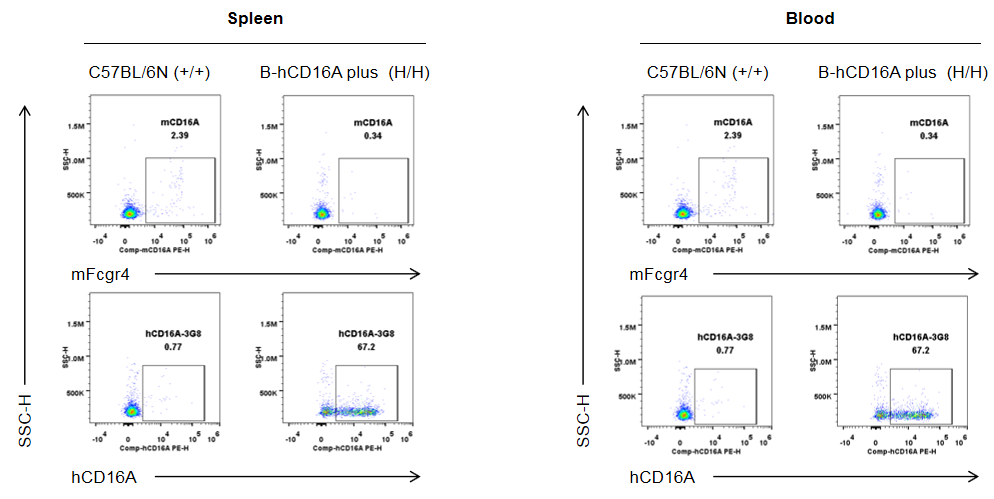
Strain specific human CD16A and mouse Fcgr4 expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6N mice and homozygous humanized B-hCD16A mice plus by flow cytometry. Splenocytes and blood cells were collected from wild-type C57BL/6N mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A mice plus(H/H) (male, 8-week-old, n=1). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse Fcgr4 antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse Fcgr4 was not detectable in NK cells of wild-type C57BL/6N mice. Human CD16A was exclusively detectable in NK cells of homozygous B-hCD16A mice plus, but not in wild-type C57BL/6N mice.
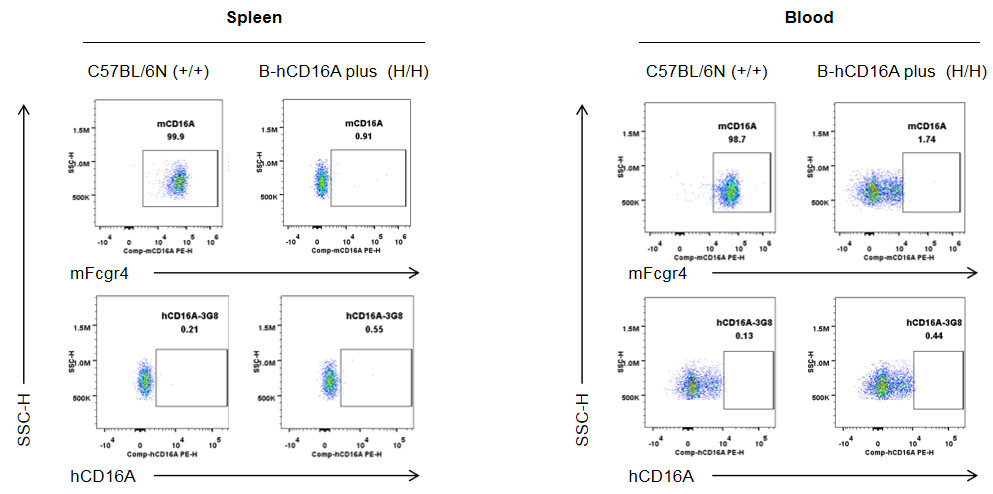
Strain specific human CD16A and mouse Fcgr4 expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6N mice and homozygous humanized B-hCD16A mice plus by flow cytometry. Splenocytes and blood cells were collected from wild-type C57BL/6N mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A mice plus(H/H) (male, 8-week-old, n=1). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse Fcgr4 antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse Fcgr4 was exclusively detectable in granulocytes of wild-type C57BL/6N mice. Human CD16A was not detectable in granulocytes of homozygous B-hCD16A mice plus.
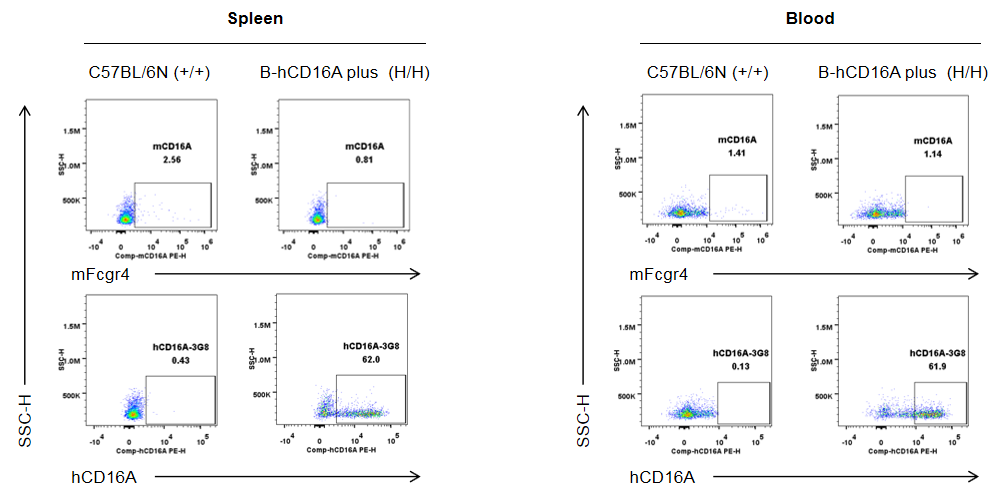
Strain specific human CD16A and mouse Fcgr4 expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6N mice and homozygous humanized B-hCD16A mice plus by flow cytometry. Splenocytes and blood cells were collected from wild-type C57BL/6N mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A mice plus(H/H) (male, 8-week-old, n=1). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse Fcgr4 antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse Fcgr4 was not detectable in monocytes of wild-type C57BL/6N mice. Human CD16A was exclusively detectable in monocytes of homozygous B-hCD16A mice plus.
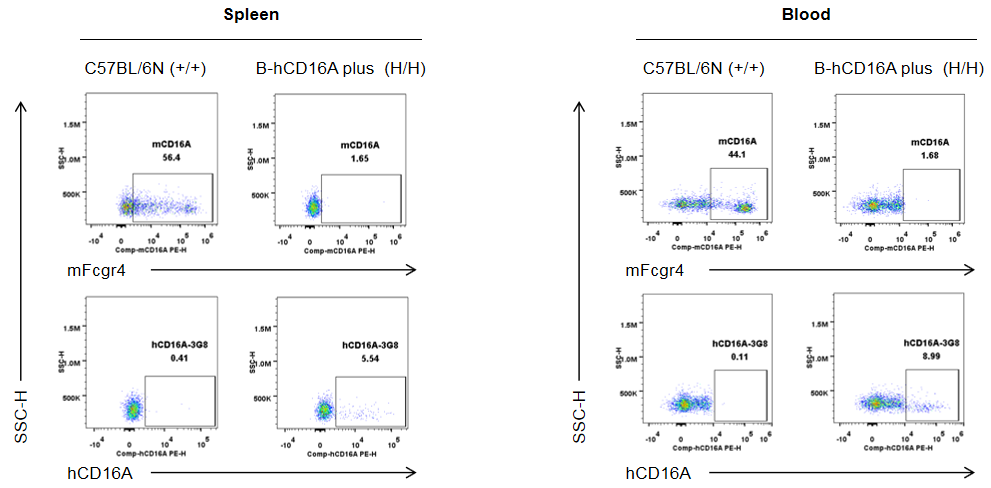
Strain specific human CD16A and mouse Fcgr4 expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6N mice and homozygous humanized B-hCD16A mice plus by flow cytometry. Splenocytes and blood cells were collected from wild-type C57BL/6N mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A mice plus(H/H) (male, 8-week-old, n=1). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse Fcgr4 antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse Fcgr4 was exclusively detectable in macrophages of wild-type C57BL/6N mice. Human CD16A was exclusively detectable in macrophages of homozygous B-hCD16A mice plus.
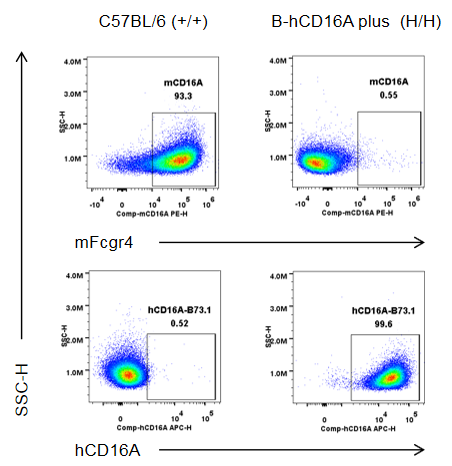
Strain specific human CD16A and mouse Fcgr4 expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6N mice and homozygous humanized B-hCD16A mice plus by flow cytometry. Peritoneal exudative macrophages(PEMs) were collected from wild-type C57BL/6N mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A mice plus(H/H) (male, 8-week-old, n=1). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse Fcgr4 antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse Fcgr4 was exclusively detectable in macrophages of wild-type C57BL/6N mice. Human CD16A was exclusively detectable in macrophages of homozygous B-hCD16A mice plus.










 京公网安备:
京公网安备: