| Strain Name |
C57BL/6N-Crbntm2(CRBN)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name | B-hCRBN mice |
| Background | C57BL/6N | Catalog number | 113236 |
|
Aliases |
MRT2, MRT2A | ||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
51185 |
||
Description
- CRBN interacts with the DNA damage-binding protein-1 (DDB1), Cullin 4 (Cul4A or Cul4B), and regulator of Cullins1 (RoC1) to form the functional E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. In this complex, CRBN functions as a substrate receptor of E3 ubiquitin ligase complex and targets proteins for proteolysis through a ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
- The CDS of human CRBN gene that encodes the full-length protein was inserted into the mouse Crbn exons 2-3. The B-hCRBN mice will express the human CRBN protein, while mouse Crbn will no longer be expressed.
- CRBN were detectable in both wild-type mice and homozygous B-hCRBN mice. The anti-CRBN antibody was cross-reactive between human and mouse.
- Mouse Crbn mRNA was detectable in cortex of wild-type mice (+/+). Human CRBN mRNA was detectable in B-hCRBN mice (H/H) but not in wild-type mice.
- Naive CD4+ T cells derived from B-hCRBN mice exhibited increased IL-2 secretion after treatment with Lenalidomide, but no such change in cells of wild-type mice.
- CC-885 exhibits marked toxicity exclusively in B-hCRBN mice, with no detectable toxicity observed in wild-type mice.
- The body weight, complete blood count and blood biochemistry of male and female B-hCRBN mice were analyzed. The main organs were dissected, weighed and analyzed by H&E staining. No obvious abnormalities were found in all the organs detected (brain, heart, lung, liver, spleen, stomach, small intestine, colon, kidney, uterus, ovary and testis).
- Tumor cell lines inoculated in B-hCRBN mice can be used to study the in vivo efficacy and safety evaluation of CRBN small molecule drugs, molecular glue drugs based on CRBN, or PROTAC drugs based on CRBN.
Targeting strategy
Gene targeting strategy for B-hCRBN mice.The CDS of human CRBN gene that encodes the full-length protein was inserted into the mouse Crbn exons 2-3. The B-hCRBN mice will express the human CRBN protein, while mouse Crbn will no longer be expressed.
mRNA expression analysis in humanized B-hCRBN mice

Strain specific analysis of CRBN mRNA expression in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous B-hCRBN mice by RT-PCR. Heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, stomach, small intestine, colon and cortex RNA was isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCRBN mice (H/H), then cDNA libraries were synthesized by reverse transcription, followed by PCR with mouse or human CRBN primers. Mouse Crbn mRNA was detectable in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Human CRBN mRNA was detectable only in homozygous B-hCRBN mice but not in wild-type mice.

Strain specific CRBN expression analysis in homozygous B-hCRBN mice by Western blot. The cortex, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, stomach, small intestine, colon and heart were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCRBN mice (H/H) and then analyzed by western blot with anti-CRBN antibody (CST, #71810). CRBN were detectable in both wild-type mice and homozygous B-hCRBN mice. The anti-CRBN antibody was cross-reactive between human and mouse.
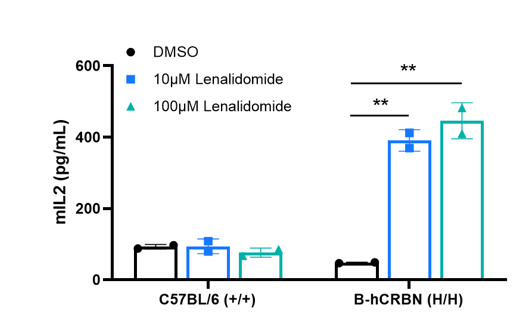
Naive CD4+ T cells derived from B-hCRBN mice exhibited increased IL-2 secretion after treatment with Lenalidomide. Naive CD4+ T cells were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCRBN mice (H/H), then stimulated with DMSO or Lenalidomide (MCE, HY-A0003) in vitro for 24 hours. The supernatants were collected, and IL-2 production was measured by ELISA (Biolegend, 431004). The results show that Lenalidomide significantly up-regulates the production of IL-2 in B-hCRBN mice, but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
In vivo toxicity of CC-885

In vivo toxicity of CC-885 in C57BL/6N mice and homozygous B-hCRBN mice. Wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous B-hCRBN mice were each divided into two groups (n=3), receiving either 5 mg/kg CC-885 (CC-885, HY-101488) or vehicle control via intraperitoneal injection. (A) Percent survival. (B) Body weight and body weight change during the treatment. Results demonstrated that all CC-885-treated B-hCRBN mice succumbed at approximately 35 hours post-injection, whereas CC-885-administered wild-type C57BL/6 mice and all control groups survived. The results show that CC-885 exhibits marked toxicity exclusively in B-hCRBN mice, with no detectable toxicity observed in wild-type mice.
Hematology analysis

Complete blood count (CBC) of C57BL/6 and B-hCRBN mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SD.
Biochemistry analysis

Biochemical test of C57BL/6 and B-hCRBN mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SD.
Gross anatomy of female and male C57BL/6 mice

The organs of female and male C57BL/6 mice (10-week-old, n=10).
Gross anatomy of female and male B-hCRBN mice

The organs of female and male B-hCRBN mice (10-week-old, n=10).
Organ weight

Average weight of the main organs of C57BL/6 and B-hCRBN mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SD.
H&E staining in C57BL/6

Histopathological analysis of organs in C57BL/6 mice. The main organs of C57BL/6 were isolated at 10 weeks of age and analyzed with H&E staining (male, n=10; female, n=10). Results showed that no obvious abnormalities were found in all of the organs (brain, heart, lung, liver, spleen, stomach, small intestine, colon, kidney, ovary, uterus and testis). Scale bar: 100 μm.
H&E staining in B-hCRBN mice

Histopathological analysis of organs in B-hCRBN mice. The main organs of B-hCRBN mice were isolated at 10 weeks of age and analyzed with H&E staining (male, n=10; female, n=10). Results showed that no obvious abnormalities were found in all of the organs (brain, heart, lung, liver, spleen, stomach, small intestine, colon, kidney, ovary, uterus and testis). Scale bar: 100 μm.










 京公网安备:
京公网安备: