B-hCD47/hGPC3 MC38
|
Common name |
B-hCD47/hGPC3 MC38 | Catalog number | 322406 |
| Aliases |
IA3; DGSX, GTR2-2, MXR7, OCI-5, SDYS, SAP, MER6, OGB, SGBS, SGBS1
|
Disease | Colon carcinoma |
|
Organism |
Mouse |
Strain | C57BL/6 |
| Tissue types | Colon | Tissue | Colon |
- Origin: The MC38 cell line is derived from C57BL/6 murine colon adenocarcinoma cells. The cell line is a commonly used murine model for colorectal carcinoma.
- Background Information: CD47, also known as integrin-associated protein (IAP), is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily containing a five-pass transmembrane attachment. CD47 is heavily glycosylated and widely expressed by hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells. CD47 interacts with several membrane integrins and also acts as a receptor for thrombospondin (THBS1). Glypicans (GPCs) are a family of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored heparan sulphate proteoglycans (HSPGs) that may play a role in the control of cell division and growth regulation.
- Gene targeting strategy: The exogenous promoter and human GPC3 coding sequence was inserted to murine Rosa26 site. The exogenous promoter and human CD47 coding sequence was inserted to replace part of murine exon 2 and all of exon 3. The insertion disrupts the endogenous murine Cd47 gene, resulting in a non-functional transcript.
- Tumorigenicity: Confirmed in B-hGPC3 mice.
- Application: B-hCD47/hGPC3 MC38 tumor models can be used for preclinical evaluation of bispecific antibody drugs targeting human CD47 and GPC3.
- Notes: The B-hCD47/hGPC3 MC38 cell line fails to form tumors in B-hSPRIA/hCD47 mice, suggesting that this cell line may also not form tumors in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. We recommend using the B-hCD47/hGPC3 MC38 #1-B06 cell line for tumor formation or efficacy studies in GPC3-related humanized mice.
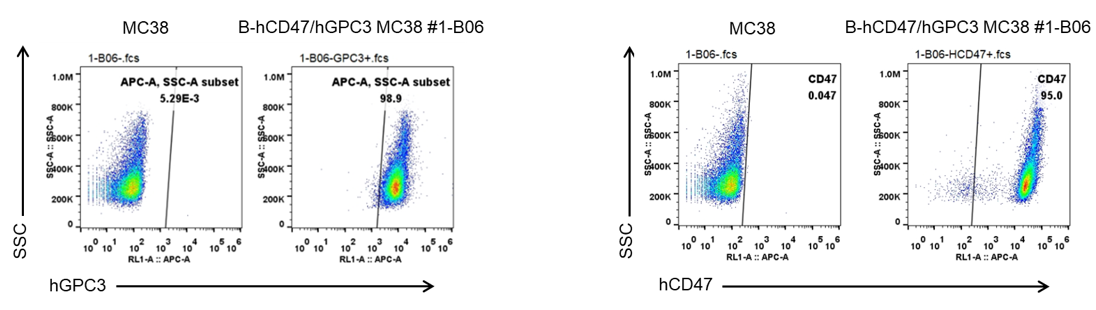
GPC3 and CD47 expression analysis in B-hCD47/hGPC3 MC38 cells by flow cytometry. Single cell suspensions from wild-type MC38 and B-hCD47/hGPC3 MC38 #1-B06 cultures were stained with species-specific anti-GPC3 antibody (Invitrogen, MA5-40988) and species-specific anti-CD47 antibody (Biolegend, 323124). Human GPC3 and CD47 were detected on the surface of B-hCD47/hGPC3 MC38 cells but not wild-type MC38 cells.
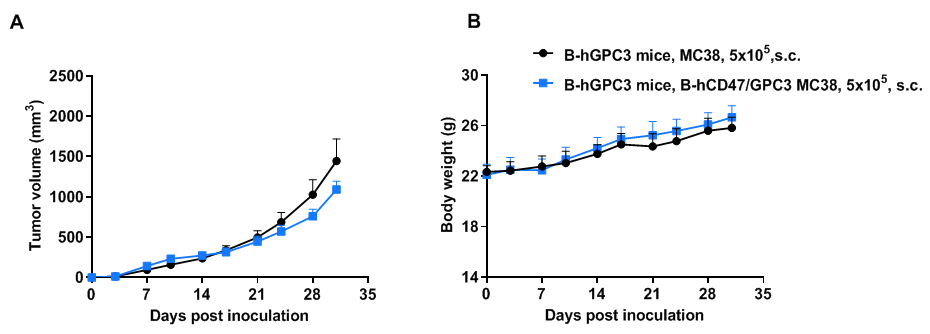
Subcutaneous tumor growth of B-hCD47/hGPC3 MC38 cells. B-hCD47/hGPC3 MC38 cells (5×105) and wild-type MC38 cells (5×105) were subcutaneously implanted into B-hGPC3 mice (H/H) (female, 7-week-old, n=6). Tumor volume and body weight were measured twice a week. (A) Average tumor volume. (B) Body weight. Volume was expressed in mm3 using the formula: V=0.5 × long diameter × short diameter2. Results indicate that B-hCD47/hGPC3 MC38 cells were able to establish tumors in vivo and can be used for efficacy studies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
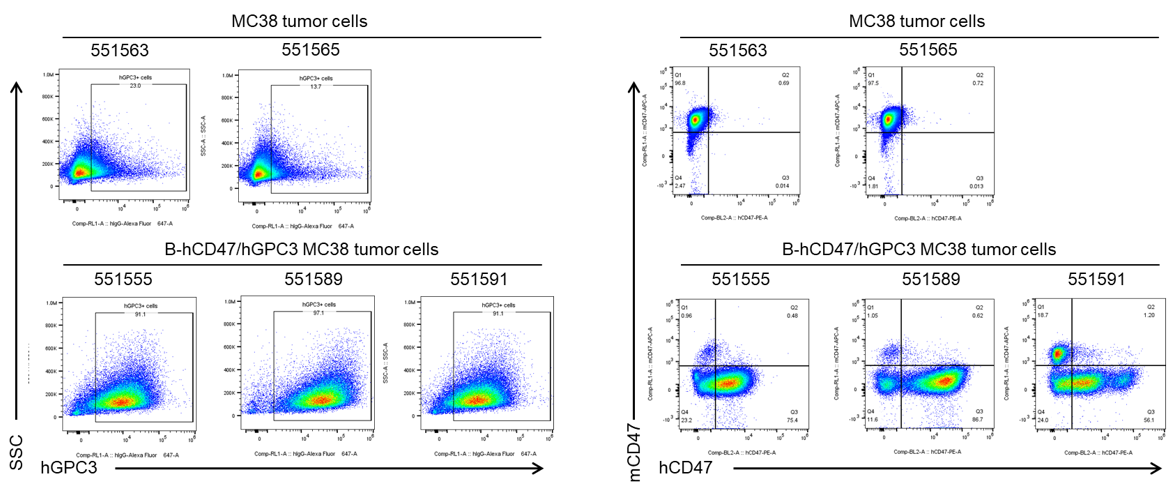
GPC3 and CD47 expression evaluated on B-hCD47/hGPC3 MC38 tumor cells by flow cytometry. B-hCD47/hGPC3 MC38 cells were subcutaneously transplanted into B-hGPC3 mice (n=6). Upon conclusion of the experiment, tumor cells were harvested and assessed for human GPC3 and CD47 expression by flow cytometry (Invitrogen, MA5-40988; Biolegend, 323124). As shown, human GPC3 and CD47 were highly expressed on the surface of tumor cells. Therefore, B-hCD47/hGPC3 cells can be used for in vivo efficacy studies evaluating novel GPC3 and CD47 therapeutics.










 京公网安备:
京公网安备: